Properties
GObject system provides properties. Properties are values kept by instances, which is a descendant of GObject, and they are open to other instances. They can be accessed with their names.
For example, GtkWindow has “title”, “default-width”, “default-height” and other properties. The string “title” is the name of the property. The name of a property is a string that begins with a letter followed by letters, digits, dash (‘-’) or underscore (’_’). Dash and underscore is used as separators but they cannot be mixed. Using dash is more efficient than underscore. For example, “value”, “double” and “double-value” are correct property names. “_value” or “-value” are incorrect.
Properties have various types of values. The type of “title” property is string. The type of “default-width” and “default-height” is integer.
Properties are set and got with functions defined in GObject.
- Properties can be set with several GObject functions.
g_object_newandg_object_setare often used. - Properties can be get with several GObject functions.
g_object_getis often used.
The functions above belongs to GObject, but they can be used for any descendant object of GObject. The following is an example of GtkWindow, which is a descendant object of GObject.
An instance is created and its properties are set with
g_object_new.
GtkWindow *win;
win = g_object_new (GTK_TYPE_WINDOW, "title", "Hello", "default-width", 800, "default-height", 600, NULL);The example above creates an instance of GtkWindow and sets the properties.
- The “title” property is set to “Hello”.
- The “default-width” property is set to 800.
- The “default-height” property is set to 600.
The last parameter of g_object_new is NULL
which is the end of the list of properties.
If you have already created a GtkWindow instance and you want to set
its title, you can use g_object_set.
GtkWindow *win;
win = g_object_new (GTK_TYPE_WINDOW, NULL);
g_object_set (win, "title", "Good bye", NULL);You can get the value of a property with
g_object_get.
GtkWindow *win;
char *title;
int width, height;
win = g_object_new (GTK_TYPE_WINDOW, "title", "Hello", "default-width", 800, "default-height", 600, NULL);
g_object_get (win, "title", &title, "default-width", &width, "default-height", &height, NULL);
g_print ("%s, %d, %d\n", title, width, height);
g_free (title);The rest of this section is about implementing properties in a descendant of GObject. It is divided into two things.
- Register a property
- Define
set_propertyandget_propertyclass method to complementg_object_setandg_object_get.
GParamSpec
GParamSpec is a fundamental object. GParamSpec and GObject don’t have parent-child relationship. GParamSpec has information of parameters. “ParamSpec” is short for “Parameter specification”.
For example,
double_property = g_param_spec_double ("value", "val", "Double value",
-G_MAXDOUBLE, G_MAXDOUBLE, 0.0,
G_PARAM_READWRITE);This function creates a GParamSpec instance, more precisely a GParamSpecDouble instance. GParamSpecDouble is a child of GParamSpec.
The instance has information:
- The value type is double. The suffix of the function name,
doubleing_param_spec_double, implies the type. - The name is “value”.
- The nick name is “val”.
- The description is “Double value”.
- The minimum value is -G_MAXDOUBLE. G_MAXDOUBLE is the maximum value which can be held in a double. It is described in GLib(2.68.1) Reference Manual – G_MAXDOUBLE and G_MINDOUBLE. You might think the lowest value of double is G_MINDOUBLE, but it’s not. G_MINDOUBLE is the minimum positive value which can be held in a double.
- The maximum value is G_MAXDOUBLE.
- The default value is 0.0.
G_PARAM_READWRITEis a flag.G_PARAM_READWRITEmeans that the parameter is readable and writable.
For further information, refer to the GObject API reference.
GParamSpec is used for the registration for GObject properties. This is extracted from tdouble.c in src/tdouble6.
#define PROP_DOUBLE 1
static GParamSpec *double_property = NULL;
static void
t_double_class_init (TDoubleClass *class) {
GObjectClass *gobject_class = G_OBJECT_CLASS (class);
gobject_class->set_property = t_double_set_property;
gobject_class->get_property = t_double_get_property;
double_property = g_param_spec_double ("value", "val", "Double value", -G_MAXDOUBLE, G_MAXDOUBLE, 0.0, G_PARAM_READWRITE);
g_object_class_install_property (gobject_class, PROP_DOUBLE, double_property);
}The variable double_property is static. GParamSpec
instance is assigned to double_property.
The function g_object_class_install_property installs a
property. It must be called after set_property and
get_property methods are overridden. These methods will be
explained later. The arguments are TDoubleClass class, PROP_DOUBLE
(property id) and GParamSpec instance. Property id is used to identify
the property in tdouble.c. It is a positive integer.
Overriding set_property and get_property class methods
Property values vary from instance to instance. Therefore, the value is stored to each instance of the object.
The function g_object_set is given a value as an
argument and stores the value. But how does g_object_set
know the instance to store? It is compiled before the object is made.
So, it doesn’t know where to store the value at all. That part needs to
be programmed by the writer of the object with overriding.
The function g_object_set first checks the property and
value, then it creates GValue (generic value) from the value. And it
calls a function pointed by set_property in the class. Look
at the diagram below.
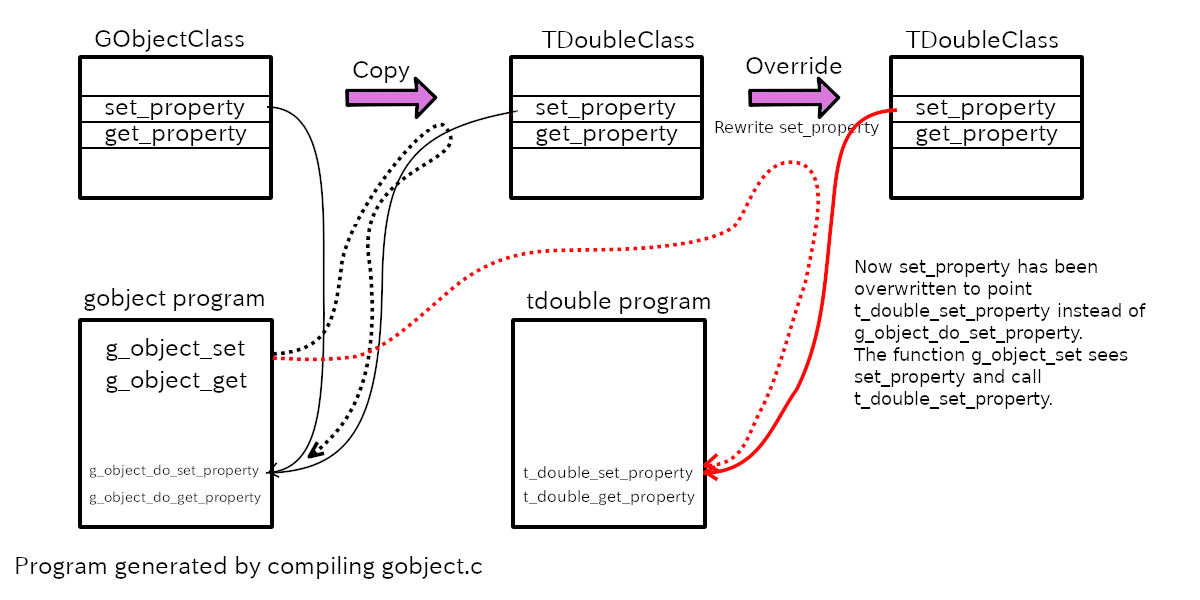
The member set_property in GObjectClass class points
g_object_do_set_property in GObject program, which is made
by compiling gobject.c. The GObjectClass part of the
TDoubleClass structure (it is the same as TDoubleClass because
TDoubleClass doesn’t have its own area) is initialized by copying from
the contents of GObjectClass. Therefore, set_property in
TDoubleClass class points g_object_do_set_property in
GObject program. But g_object_do_set_property doesn’t store
the value to the TDouble instance. The writer of TDouble object makes
t_double_set_property function in tdouble.c.
And assigns the address of t_double_set_property to
set_property in TDoubleClass class. It is shown with a red
curve in the diagram. As a result, g_object_set calls
t_double_set_property instead of
g_object_do_set_property (red dotted curve) and the value
will be stored in the TDouble instance. See the function
t_double_class_init above. It changes the member
gobject_class->set_property to point the function
t_double_set_property. The function
g_object_set sees the TDoubleClass and call the function
pointed by the member set_property.
The program of t_double_set_property and
t_double_get_property will shown later.
GValue
GValue is generic value. GValue consists of type and value.
The type is any Gtype. The table below shows some GType, but not all.
| GType | C type | type name | notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| G_TYPE_CHAR | char | gchar | |
| G_TYPE_BOOLEAN | int | gboolean | |
| G_TYPE_INT | int | gint | |
| G_TYPE_FLOAT | float | gfloat | |
| G_TYPE_DOUBLE | double | gdouble | |
| G_TYPE_STRING | gchararray | null-terminated Cstring | |
| G_TYPE_PARAM | GParam | GParamSpec | |
| G_TYPE_OBJECT | GObject | ||
| G_TYPE_VARIANT | GVariant |
If the type of a GValue value is
G_TYPE_DOUBLE, value can be get with
g_value_get_double function.
GValue value;
value = ... ... ... (a GValue object is assigned. Its type is double.)
double v;
v = g_value_get_double (&value);Conversely, you can set GValue value with
g_value_set_double.
g_value_set_double (value, 123.45);Refer to GObject API Reference – GValue for further information.
t_double_set_property and t_double_get_property
g_object_set makes GValue from the value of the property
given as an argument. And calls a function pointed by
set_property in the class. The function is declared in
GObjectClass structure.
struct _GObjectClass
{
... ... ...
... ... ...
/* overridable methods */
void (*set_property) (GObject *object,
guint property_id,
const GValue *value,
GParamSpec *pspec);
void (*get_property) (GObject *object,
guint property_id,
GValue *value,
GParamSpec *pspec);
... ... ...
... ... ...
};t_double_set_property just get the value from GValue
value and store it to the TDouble instance.
static void
t_double_set_property (GObject *object, guint property_id, const GValue *value, GParamSpec *pspec) {
TDouble *self = T_DOUBLE (object);
if (property_id == PROP_DOUBLE)
self->value = g_value_get_double (value);
else
G_OBJECT_WARN_INVALID_PROPERTY_ID (object, property_id, pspec);
}- 3: Casts
objectto TDouble objectself. - 6: Set
self->value. The assigned value is got withg_value_get_doublefunction.
In the same way, t_double_get_property stores
self->value to GValue.
static void
t_double_get_property (GObject *object, guint property_id, GValue *value, GParamSpec *pspec) {
TDouble *self = T_DOUBLE (object);
if (property_id == PROP_DOUBLE)
g_value_set_double (value, self->value);
else
G_OBJECT_WARN_INVALID_PROPERTY_ID (object, property_id, pspec);
}Notify signal
GObject emits “notify” signal when a property is set. When you connect “notify” signal to your handler, you can specify a detail which is the name of the property. The detail is added to the signal name with the delimiter “::”.
g_signal_connect (G_OBJECT (d1), "notify::value", G_CALLBACK (notify_cb), NULL);If you don’t specify details, the handler is called whenever any properties are set. So, usually the detail is set.
Notify signal doesn’t mean that the value of the property is changed.
It is emitted even if the same value is set. You might want to emit the
notify signal only when the property is actually changed. In that case,
you define the GPramSpec with G_PARAM_EXPLICIT_NOTIFY flag.
Then, the notify signal isn’t emitted automatically. Instead you call
g_object_notify_by_pspec function to emit “notify” signal
explicitly when the value of the property is actually changed.
It is possible to make setter and getter for the property. But if you just set the instance member in your setter, notify signal isn’t emitted.
void
t_double_set_value (TDouble *self, double value) {
g_return_if_fail (T_IS_DOUBLE (self));
self->value = value; /* Just set d->value. No "notify" signal is emitted. */
}Users must be confused if they want to catch the “notify” signal. One
solution is use g_object_set in your setter. Then, notify
signal will be emitted even if a user uses the setter function.
void
t_double_set_value (TDouble *d, double value) {
g_return_if_fail (T_IS_DOUBLE (d));
g_object_set (d, "value", value, NULL); /* Use g_object_set. "notify" signal will be emitted. */
}The other solution is use g_object_notify_by_pspec to
emit the signal explicitly. Anyway, if you make a setter for your
property, be careful about notify signal.
Define more than one property
If you define more than one property, use an array of property id. It
is good for you to see Gtk source files such as gtklabel.c.
GtkLabel has 18 properties.
There’s an example in src/tdouble6 directory.
Exercise
Make TInt object. It is like TDouble but the value type is int. Define “div-by-zero” signal and “value” property.
Compare your answer to the files in src/tint directory.